What is a magnetic flow meter and how does it work?
Magnetic flow meters, also known as electromagnetic flow meters or magmeters, are essential instruments for accurately measuring liquid flow in a wide range of industrial applications.
On this page we cover all key aspects of this technology: from the working principle based on electromagnetic induction, advantages and limitations and typical applications.
We also answer frequently asked questions such as: "What is a magnetic flow meter and how does it work?" and "Why should I choose a magnetic flow meter for my application?".
What is a magnetic flow meter and how does it work?
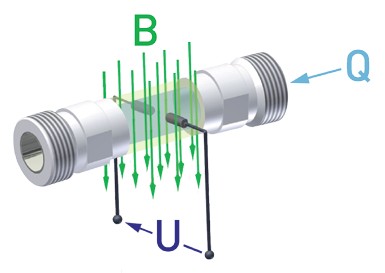
A magnetic flow meter measures fluid flow through a straight pipe in the sensor. The cylindrical pipe creates a constant and directional magnetic field across the diameter of the flow path. The flow meter is surrounded by an iron-core, permanent magnet that generates a magnetic field with lines of magnetic flux passing vertically through the pipe and the flowing fluid.
According to Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction, a voltage is induced in a conductor moving at right angles through a magnetic field, and this voltage is proportional to the conductor's velocity. This method requires the liquid to be sufficiently conductive (at least 20 µS/cm) for the MAG-VIEW magnetic flow meter.
Therefore, liquids like demineralized water, oil, or other non-conductive fluids are not suitable for this method.
Key components:
- Measuring tube: Typically stainless steel with an insulating liner (such as PTFE or hard rubber) for chemical compatibility and electrical isolation.
- Magnetic coils: Generate a strong magnetic field perpendicular to the flow direction.
- Electrodes: Capture the induced voltage, often made from stainless steel or Hastelloy depending on chemical resistance needs.
- Transmitter: Converts the measurement signal into a standardized output for display or communication.
Why choose a magnetic flow meter?
This type of meter offers many unique advantages:
- Accuracy: Typically 0.2 to 1% of the measured value, making this technology in the top of precise for liquid flow.
- No pressure loss: most of the times it's an open pipe that creates no constrictions, some design an narrowing is applied for gainig more accuracy.
- Low to no maintenance: There are no moving parts that can wear or get stuck. Maintenance is usually limited to periodic cleaning of the electrodes.
- Suitable for dirty or aggressive liquids: With robust linings and chemically resistant electrodes, even slurry, wastewater, salts, and acids can be reliably measured.
- Insensitive to pressure, temperature, and viscosity: Fluctuations in medium temperature or pressure (as long as within specifications) have almost no effect on the measurement.
- Versatile: Available in diameters from a few millimeters up to more than 50 or 100cm, suitable for small labs or the largest water treatment plants.
In summary: if you want to measure water-based, conductive liquids, the magnetic flow meter is often the most durable and reliable choice.
Make liquid flow visible, Buy now the Electromagnetic Flow Meter
How do the components of an electromagnetic flow meter work together?
A magmeter consists of several specialized parts that must work together flawlessly for optimal performance:
- Measuring tube: Made from stainless steel and lined (such as PTFE or PFA) for electrical insulation and resistance to aggressive substances.
- Coils: Ensure a magnetic field in the tube. Modern meters often use pulsed DC coils to minimize interference.
- Electrodes: Made of chemically resistant materials, placed at optimal locations to detect the highest voltage from flow.
- Transmitter unit: Receives the measured voltage and converts it via the PCB board into an analog or digital output signal (such as 4-20 mA, Profibus, Modbus).
What applications are electromagnetic flow meters suitable for?
Drinking Water & Wastewater Utilities
Accurate measurement of distribution water, leak detection, monitoring of treated and untreated wastewater, effluent control, and sludge flow management.Process & Chemical Industry
Precise dosing of chemicals, acids, alkalis, and industrial (waste)water. Ideal for process optimization and safety compliance.Food & Beverage Industry
Hygienic flow measurement for dairy, beer, soft drinks, and CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems. Suitable for high-temperature and sanitary cleaning processes.Mining, Minerals, Pulp & Paper
Reliable flow measurement of slurries, abrasive fluids, and suspensions using wear-resistant liners for long-term durability.General Industrial Applications
Monitoring of cooling and wastewater, dosing of mold release agents, and other industrial liquids.Cleaning & Concrete Industry
Controlled dosing of detergents, cleaning agents, additives, and colorants for consistent product quality.Agriculture & Livestock
Efficient dosing of water, fertilizers, pesticides, fungicides, and liquid feed supplements to support sustainable farming.Exhaust Gas Treatment
Accurate dosing of AdBlue (DEF) for emission control in diesel engines and industrial exhaust systems (nox scrubbing process).
Benefits of electromagnetic flow meters
- Accuracy: Up to ±0.2-5% on top models.
- No pressure loss: Unobstructed tube, no moving parts.
- Excellent for contaminated media: Suitable for sludge, slurry, sand, liquid manure, chemicals.
- Maintenance free: No moving parts, low maintenance costs.
- Chemical resistance: Materials such as PTFE or Hastelloy allows use with aggressive liquids.
- Fast response times: Ideal for process control and dosing systems.
- Wide range: From a few liters per hour to thousands of cubic meters per hour.
Disadvantages and limitations of magnetic flow meters
 Only suitable for conductive liquids: Oils, gases, and ultrapure water are excluded.
Only suitable for conductive liquids: Oils, gases, and ultrapure water are excluded.- Conductivity threshold: Usually requires >20 μS/cm.
- Correct installation is crucial: The measuring tube must always be full; air bubbles can cause disturbance.
- Interference: Strong electromagnetic fields (e.g., from large motors) can disrupt measurement. Proper grounding and cabling are important.
- Purchase price: Higher than classic mechanical meters, but lower operational costs usually offset this.
Market trends and figures (2024)
- Market structure: 25% of all industrial flow measurements worldwide use magmeters.
- Increasing digitization: Modern magmeters are often smart (IoT-ready), equipped with diagnostics, wireless connectivity, and automatic calibration.
- Growth in use cases: Demand is rising especially in water management, wastewater, food industry, and chemicals.
- Major brands/manufacturers: Endress+Hauser, ABB, Siemens, SIKA, Krohne, Yokogawa, Honeywell, Emerson, Schneider Electric.
- Different types: Inline (high accuracy), insertion (for large pipes or temporary setups), low-flow meters for laboratories/medical use.
Comparison: electromagnetic flow meters vs. alternative technologies

- Ultrasonic flow meters: Use sound waves, also measure non-conductive liquids and gases. Clamp-on installation is possible but more sensitive to solids or air bubbles.
- Coriolis flow meters: Measure mass and density, extremely accurate but expensive and sensitive to gas pockets.
- Vortex/Impeller/PD meters: Also work for non-conductive fluids, inexpensive but more susceptible to wear/blockage, not suited for abrasive, dirty media.
Selection and installation tips
- Conductivity: Is your liquid suitable in terms of conductivity?
- Right liner/electrodes: Choose materials compatible with chemicals and temperatures to be measured.
- Always a full pipe: The measuring tube must not be partially empty; placement and installation (orientation) is key.
- Flow profile: Preferably a straight section of at least 10x the diameter before and 5x after the meter.
- Protection from interference: Ensure proper grounding and shielded cabling.
- Certification: Pay attention to ATEX or other certifications for hazardous or food-grade applications.
Where to buy magnetic flow meter?
In our online webshop our MAG-VIEW instruments are mainly used with Stainless steel 1.4404 (AISI 316L)
Our MVM-QAH models have Hastelloy C© material for aggressive media for long durability.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ) – Magnetic Flow Meters
What is a magnetic flow meter and how does it work?
A magmeter measures the volume of conductive liquids by electromagnetic induction: the liquid passes through a magnetic field and a voltage proportional to the flow is induced and detected by electrodes.
Can a magmeter measure oil, gases, or air?
No, only liquids with sufficient conductivity (usually water-based) can be measured. Oils, gases, and ultrapure water are excluded.
Are electromagnetic flow meters accurate?
Yes, accuracy ranges from ±0.2 to ±1% of the measured value.
Is maintenance required?
Minimal; usually periodic cleaning of the electrodes to prevent fouling or corrosion.
Can I measure bidirectional flow?
Yes, some magmeters can measure both forward and reverse flow.
Are these meters sensitive to temperature or pressure?
Hardly. Only the mechanical limits of the material or electrodes may limit use.
Does a magmeter cause pressure loss?
No, or minimal due to small narrowing in the tube.
What is the maximum flow range?
From a few liters/hour to thousands of m³/h, depending on the size of the tube.
 Summary and conclusion
Summary and conclusion
Thanks to low maintenance operation, application with conductive (including dirty or abrasive) media, fast response, electromagnetic flowmeters are functional in water and process industries.
For non-conductive liquids, you can use our liquid Vortex Flow meters. These meters utilize the vortex shedding principle, conductivity is not needed.

> MAG-VIEW Magnetic Flow Meter
- Flow range up to 250 l/min (8 models max range; 1, 2, 5, 20, 30, 60, 200, 250 l/min)
- Material Stainless Stainless steel 1.4404 (AISI 316L) or for more aggressive media Hastelloy C©
- Output Analog 4-20mA or Frequency
- Maintenance-free no moving parts
- Medium Water and other conductive liquids
- Free cross section Very low pressure drop
- Mounting In any position